windows 虚拟文件系统 虚拟文件系统VFS的工作原理及应用
windows 虚拟文件系统,随着计算机技术的不断发展,虚拟化技术也逐渐成为企业信息化建设的重要组成部分。其中Windows虚拟文件系统(VFS)作为Windows操作系统中的一种重要虚拟化技术,具有非常重要的应用意义。本文将重点介绍Windows VFS的工作原理及其应用,以帮助读者更深入了解这一技术的实现方式与优势,为企业信息化建设提供更有价值的参考。
虚拟文件系统VFS的工作原理及应用
前言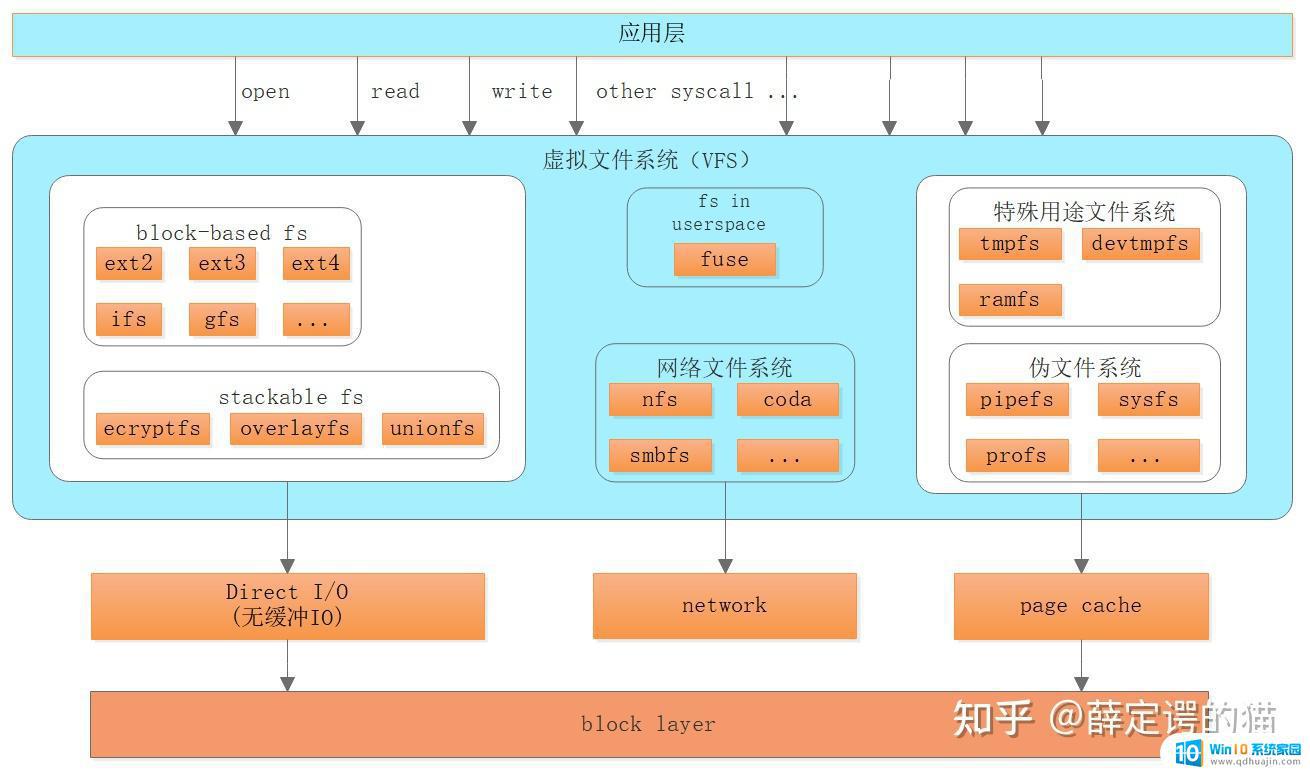 VFS 是什么
VFS 是什么虚拟文件系统,简称 VFS(Virtual Filesystem),是一个内核软件层。
VFS 的作用概括地讲,VFS 有两个作用:
处理与 Unix 标准文件系统相关的所有系统调用为各种文件系统提供一个通用的接口VFS 支持的文件系统类型以下列出以下常见的文件系统类型,本文暂时不对其进行详细分析。
磁盘文件系统ext2,ext3。···网络文件系统类型nfs,smbfs,···特殊文件系统tmpfs,ramfs,···伪文件系统procfs,sysfs,···VFS 的设计思想VFS 设计的初衷就是要支持所有的文件系统,所以它的设计思想其实就是以面向对象的方式,设计一个通用的文件模型,出于效率考虑,VFS 还是 C 语言写的。在通用文件系统模型中,每个目录也被当作一个文件,可以包含若干文件和其他的子目录。因此,Linux 有一句经典的话:一切皆文件。
关键数据结构介绍Linux VFS 抽象出 4 种类型的数据结构,实现将不同类型的文件系统挂载到目录结构中。
超级块对象对于磁盘类文件系统,超级块是存放在磁盘上的文件系统控制块。里面存放已安装文件系统的有关信息,换句话说,一个超级块描述了一个具体的文件系统信息,里面的信息十分重要,也叫元数据,与普通的文件数据相比,元数据丢失会损坏整个文件系统,导致无法挂载之类的问题。
struct super_block {
struct list_head s_list; // 超级快链表指针
dev_t s_dev; // 设备表示符
unsigned char s_blocksize_bits; //以位为单位的块的大小
unsigned long s_blocksize; //以字节为单位的块大小
loff_t s_maxbytes; //文件大小的上限
struct file_system_type *s_type; //指向文件系统的file_system_type 数据结构的指针
const struct super_operations *s_op; //超级块方法
const struct dquot_operations *dq_op; //磁盘限额方法
const struct quotactl_ops *s_qcop; //限额控制方法
const struct export_operations *s_export_op; //导出方法
unsigned long s_flags; //登录标志
unsigned long s_magic; //文件系统的魔术字
struct dentry *s_root; //目录登录点
struct rw_semaphore s_umount; //卸载信号量
int s_count; //超级块引用计数
atomic_t s_active; //活动引用记数
#ifdef CONFIG_SECURITY
void *s_security; //安全模块
#endif
const struct xattr_handler **s_xattr;
struct list_head s_inodes; //把所有索引对象链接在一起,存放的是头结点
struct hlist_bl_head s_anon; //匿名目录项
struct list_head s_mounts; /* list of mounts; _not_ for fs use */
struct block_device *s_bdev; //相关的块设备
struct backing_dev_info *s_bdi;
struct mtd_info *s_mtd;
struct hlist_node s_instances; //该类型文件系统
unsigned int s_quota_types; /* Bitmask of supported quota types */
struct quota_info s_dquot;//限额相关选项
struct sb_writers s_writers;
char s_id[32]; /* Informational name */
u8 s_uuid[16]; /* UUID */
void *s_fs_info; /* Filesystem private info */
unsigned int s_max_links;
fmode_t s_mode;
u32 s_time_gran;
struct mutex s_vfs_rename_mutex; /* Kludge */
char *s_subtype;
char __rcu *s_options;
const struct dentry_operations *s_d_op; /* default d_op for dentries */
int cleancache_poolid;
struct shrinker s_shrink; /* per-sb shrinker handle */
atomic_long_t s_remove_count;
int s_readonly_remount;
struct workqueue_struct *s_dio_done_wq;
struct hlist_head s_pins;
struct list_lru s_dentry_lru ____cacheline_aligned_in_smp;
struct list_lru s_inode_lru ____cacheline_aligned_in_smp;
struct rcu_head rcu;
int s_stack_depth;
};
索引节点对象(inode)索引节点存放关于具体文件的一般信息。对于磁盘类文件系统,索引节点也是存放在磁盘上的文件控制块。每个索引节点都有一个索引节点号,这个节点号唯一地标识了文件系统中的文件。
struct inode {
umode_t i_mode; //访问权限控制
unsigned short i_opflags;
kuid_t i_uid; //使用者的id
kgid_t i_gid; //使用组id
unsigned int i_flags; //文件系统标志
#ifdef CONFIG_FS_POSIX_ACL
struct posix_acl *i_acl;
struct posix_acl *i_default_acl;
#endif
const struct inode_operations *i_op; //指向索引结点操作结构体的指针
struct super_block *i_sb; //指向inode所属文件系统的超级块的指针
struct address_space *i_mapping; //相关的地址映射
#ifdef CONFIG_SECURITY
void *i_security; //安全模块
#endif
unsigned long i_ino; //索引结点号。通过ls -i命令可以查看文件的索引节点号
union {
const unsigned int i_nlink; //硬链接数
unsigned int __i_nlink;
};
dev_t i_rdev; //实际设备标识符号
loff_t i_size; //以字节为单位
struct timespec i_atime; //最后访问时间
struct timespec i_mtime; //最后修改时间
struct timespec i_ctime; //最后改变时间
spinlock_t i_lock; /* i_blocks, i_bytes, maybe i_size */
unsigned short i_bytes; //使用的字节数
unsigned int i_blkbits; 以位为单位的块大小
blkcnt_t i_blocks; //文件的块数
#ifdef __NEED_I_SIZE_ORDERED
seqcount_t i_size_seqcount;
#endif
unsigned long i_state; //状态标志
struct mutex i_mutex;
unsigned long dirtied_when; //首次修改时间
unsigned long dirtied_time_when;
struct hlist_node i_hash; //散列表
struct list_head i_wb_list; /* backing dev IO list */
struct list_head i_lru; /* inode LRU list */
struct list_head i_sb_list; //链接一个文件系统中所有inode的链表
union {
struct hlist_head i_dentry; //目录项链表
struct rcu_head i_rcu;
};
u64 i_version; //版本号
atomic_t i_count; //引用计数
atomic_t i_dio_count;
atomic_t i_writecount; //写者计数
#ifdef CONFIG_IMA
atomic_t i_readcount; /* struct files open RO */
#endif
const struct file_operations *i_fop; /* former ->i_op->default_file_ops */
struct file_lock_context *i_flctx;
struct address_space i_data; //设备地址映射
struct list_head i_devices; //块设备链表
union {
struct pipe_inode_info *i_pipe; //管道信息
struct block_device *i_bdev; //块设备
struct cdev *i_cdev; //字符设备
};
__u32 i_generation; //索引节点版本号
#ifdef CONFIG_FSNOTIFY
__u32 i_fsnotify_mask; /* all events this inode cares about */
struct hlist_head i_fsnotify_marks;
#endif
void *i_private; /* fs or device private pointer */
};
目录项对象(dentry)存放 dentry 与对应文件链接的有关信息,每个 dentry 代表路径中的一个特定部分,每个磁盘类文件系统以自己的方式将目录项信息存放在磁盘上。
struct dentry {
/* RCU lookup touched fields */
unsigned int d_flags; /* protected by d_lock */
seqcount_t d_seq; /* per dentry seqlock */
struct hlist_bl_node d_hash; /* lookup hash list */
struct dentry *d_parent; /* parent directory */
struct qstr d_name;
struct inode *d_inode; /* Where the name belongs to - NULL is negative */
unsigned char d_iname[DNAME_INLINE_LEN]; /* small names */
/* Ref lookup also touches following */
struct lockref d_lockref; /* per-dentry lock and refcount */
const struct dentry_operations *d_op;
struct super_block *d_sb; /* The root of the dentry tree */
unsigned long d_time; /* used by d_revalidate */
void *d_fsdata; /* fs-specific data */
struct list_head d_lru; /* LRU list */
struct list_head d_child; /* child of parent list */
struct list_head d_subdirs; /* our children */
/*
* d_alias and d_rcu can share memory
*/
union {
struct hlist_node d_alias; /* inode alias list */
struct rcu_head d_rcu;
} d_u;
};
文件对象(file)存放被打开文件与进程间交互的信息,这类信息仅当进程访问文件期间存放在内存中。
struct file {
union {
struct llist_node fu_llist; //每个文件系统中被打开的文件都会形成一个双链表
struct rcu_head fu_rcuhead;
} f_u;
struct path f_path;
struct inode *f_inode; /* cached value */
const struct file_operations *f_op; //指向文件操作表的指针
spinlock_t f_lock;
atomic_long_t f_count; //文件对象的使用计数
unsigned int f_flags; //打开文件时所指定的标志
fmode_t f_mode; //文件的访问模式
struct mutex f_pos_lock;
loff_t f_pos; //文件当前的位移量
struct fown_struct f_owner;
const struct cred *f_cred;
struct file_ra_state f_ra; //预读状态
u64 f_version; //版本号
#ifdef CONFIG_SECURITY
void *f_security; //安全模块
#endif
/* needed for tty driver, and maybe others */
void *private_data;
#ifdef CONFIG_EPOLL
/* Used by fs/eventpoll.c to link all the hooks to this file */
struct list_head f_ep_links;
struct list_head f_tfile_llink;
#endif /* #ifdef CONFIG_EPOLL */
struct address_space *f_mapping; //页缓存映射
} __attribute__((aligned(4))); /* lest something weird decides that 2 is OK */
struct file_handle {
__u32 handle_bytes;
int handle_type;
/* file identifier */
unsigned char f_handle[0];
};
数据结构组织关系图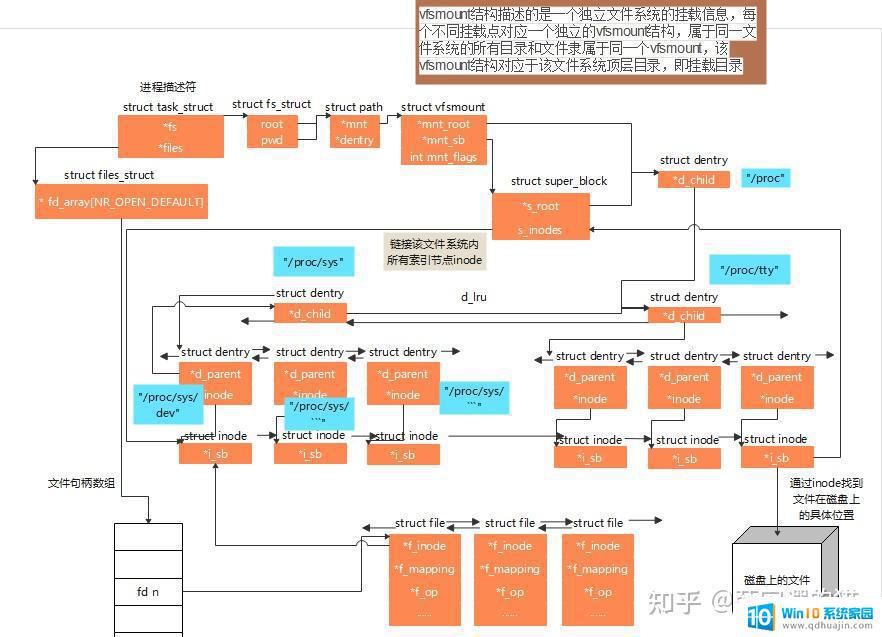
如果文章对你有用,求个关注,感谢!
综上所述,Windows虚拟文件系统作为操作系统中重要的一部分,能够有效地管理所有不同类型的文件系统,提高了操作系统内核的灵活性和可扩展性。同时其应用还涉及到高速缓存、文件加密、虚拟化等方面,为系统性能提升和数据安全提供了重要保障。
windows 虚拟文件系统 虚拟文件系统VFS的工作原理及应用相关教程
热门推荐
电脑教程推荐
- 1 windows系统经常无响应,怎么弄 电脑桌面无响应怎么解决
- 2 windows电脑c盘怎么清理 Windows 清理C盘的步骤
- 3 磊科路由器桥接 磊科无线路由器桥接设置详解
- 4 u盘提示未格式化 raw RAW格式U盘无法格式化解决方法
- 5 笔记本新装win 10系统为什么无法连接wifi 笔记本无线网连不上如何解决
- 6 如何看win几系统 win几系统查看方法
- 7 wind10如何修改开机密码 电脑开机密码多久更改一次
- 8 windows电脑怎么连手机热点 手机热点连接笔记本电脑教程
- 9 win系统如何清理电脑c盘垃圾 Windows 如何解决C盘红色警告
- 10 iphone隐藏软件怎么显示出来 苹果手机应用隐藏教程
win10系统推荐
- 1 萝卜家园ghost win10 64位家庭版镜像下载v2023.04
- 2 技术员联盟ghost win10 32位旗舰安装版下载v2023.04
- 3 深度技术ghost win10 64位官方免激活版下载v2023.04
- 4 番茄花园ghost win10 32位稳定安全版本下载v2023.04
- 5 戴尔笔记本ghost win10 64位原版精简版下载v2023.04
- 6 深度极速ghost win10 64位永久激活正式版下载v2023.04
- 7 惠普笔记本ghost win10 64位稳定家庭版下载v2023.04
- 8 电脑公司ghost win10 32位稳定原版下载v2023.04
- 9 番茄花园ghost win10 64位官方正式版下载v2023.04
- 10 风林火山ghost win10 64位免费专业版下载v2023.04